The highlights of the simulation solutions in this area for you at a glance.
Multi-Component Flash Boiling for Injector and In-Cylinder Flow Simulations
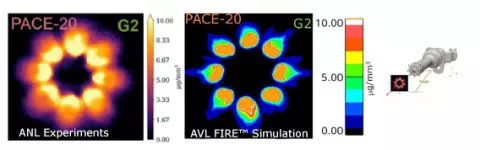
Simulating the complete chain of events - from internal injection nozzle flow, fuel injection into the combustion chamber, generation of wall film, combustion and emission formation - is a challenging task which can now be performed significantly more conveniently thanks to FIRE M 2023 R1 while considering even more physics. All related simulations and simulation models access the extended Material Property Database enabling the handling of multi-component surrogate fuels (fossil resource based, e-, bio-, syn-fuels). Extensions of the fuel evaporation model take care of flash boiling, which occurs when injecting under elevated temperatures.
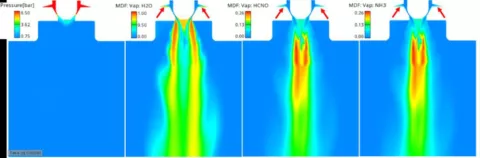
Thermolysis and Hydrolysis Model in the AVL FIRE™ M Multiphase Framework
For diesel-powered vehicles, the emission of nitrogen oxides (NOx) is a particular challenge.
This new release of FIRE M allows you to simulate the decomposition of the Urea-Water solution along with the activated General Gas Phase Reaction (GGPR) module considering that the thermolysis-hydrolysis process is happening simultaneously, in the multiphase framework This improves the predictiveness of the simulation solution.
Table Generation for ICE Combustion Simulations using ECFM-3Z
The tools needed for the generation of laminar flame speed and auto ignition delay tables have been packed into a GUI-driven workflow, which is made available with the release 2023 R1. The tables can be used directly for combustion simulation using the ECFM-3Z model of FIRE M.
Further Highlights in AVL FIRE™ M 2023 R1
UI-based differencing of FAME projects: The 2023 R1 release of FAME takes the first step in making it easy for you to compare FAME projects utilizing the graphical user interface to visualize the differences.
Melting and solidification model: This new release models the mass transfer of a melting and solidification problem in the multiphase framework of FIRE M.
TABKIN table generation: Table generation is now available also under Windows.
1D/3D Coupling Interface: A FIRE M/GT Power (a product of GAMMA TECHNOLOGIES Inc.) interface is now available with FIRE M.
Dual-Fuel and Gas Engine
The latest engine and engineering enhanced cylinder models enable the investigation of alternative fuels. It is possible to combust multiple fuels, to use gaseous fuels, and to change the fuel during a running simulation.
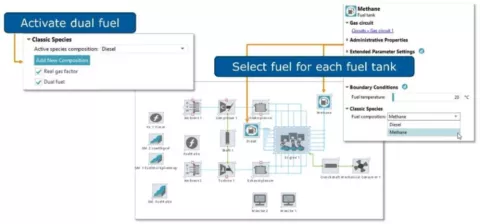
Engineering Enhanced Cylinder Models
The engineering enhanced gasoline cylinder (EEGC) has been enhanced with new functionalities:
- The fuel treatment has been improved by utilizing the gas property generator to specify the fuel composition according to the fuel properties given by fuel specification sheets. This allows you to consider oxygenated gasoline fuels as well as various compositions of gaseous fuels in a more accurate manner.
- A new CNG combustion model has been introduced along with the improvement of the fuel treatment. The engine-out emission models are extended with a CNG-specific THC/CH4 sub-model. You can now choose between hydrocarbon emission models for gasoline or CNG combustion via a drop-down menu in the EEGC GUI.
- The cylinder component now offers the possibility to configure two different fuels (e.g. gasoline and CNG). You can select your fuel before starting a simulation and you also can switch between fuels during a simulation run. With that, you can tackle bi-fuel applications in SiL and HiL environments without having to restart your model.
The engineering enhanced diesel cylinder (EEDC) component has been further enhanced with additional models and parameters:
- In the fuel injection system you can now choose between two different types of injectors, giving more precision in predicting the injected fuel amount.
- The injection coordinator, which differentiates between the various pilot, main and post injections, can now be tuned with external parameters to improve its robustness.
- The friction model has been improved to consider the influence of the oil temperature during the warmup phase.
- A new model has been added to the EEDC to provide information about possible misfiring. The parameterization wizard has been further enhanced. It now allows the calibration of the peak cylinder temperature and the emissions of CO, THC and soot.
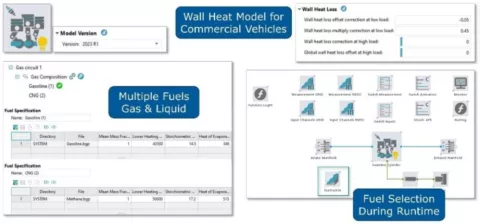
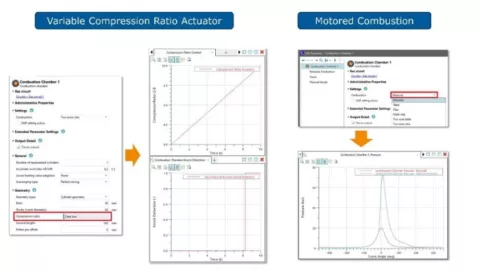
Motored Combustion and Variable Compression Ratio
The Combustion Chamber component has been enhanced with two functions.
- Motored combustion: The combustion chamber can be operated without an actual combustion model. The intake of any gas, its compression and exhaust can be simulated in an isolated manner. With that, the behavior of reciprocating compressors can be mimicked.
- Variable compression ratio: The compression ratio can be actuated via a data bus channel. This enables investigating engine concepts.